What is Primary vs Secondary Data
Introduction
You have chosen a very interesting research topic for your research and now you want to execute your study. Like every researcher, your main objective would be to obtain relevant and appropriate data for your research. However, when it is about the methods of data collection, primary and secondary data are two of the most frequently used data collection methods in a thesis. Both of these data collection methods embed different procedures and characteristics. Whether qualitative or quantitative research design, research is incomplete without implementation of primary or secondary sources. The following page is going to shed light on the insights of primary and secondary data collection methods
What is Primary Data?
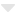
The data that is accumulated directly from first-hand experiences is known as Primary data. This method is used by authors for obtaining data for a particular kind of research. This kind of data collection method is also regarded as a raw material since it comprises original data from first source. In this procedure, the approach of the researcher is tailored to specific motives. Using primary data collection can be a hectic choice but it assures guaranteed results in most cases. The most common types of primary data that are used by researchers in their thesis projects are as follows;
- Interview (telephone, personal interview, e-mail)
- Experiments
- Self-administered surveys and questionnaires
- Diary entries, letters, and other correspondence
- Case studies
- Field surveillance
- Ethnographic research
- Action research
- Life histories
- Eyewitness accounts
- Personal narratives, memoirs
Additionally, by making use of these sources it is obvious that a researcher needs a certain group or sample to obtain this kind of data from. Hence, the researcher selects a specific sample by making use of various types of sampling techniques and procedures.
Pros and Cons of Primary Data
Just like everything in this world possess some good and bad characteristics, the same is the case with primary data collection methods.
| Pros of Primary Data | Cons of Primary Data |
|---|---|
|
Improved Accuracy |
More Limitations |
|
A Greater Level of Control |
Not Always Possible |
|
Updated Information |
Time-Consuming |
|
Owner Of The Data |
More Costly |
What is Secondary Data?
The information that has already been gathered previously for some other motive but has some significance to research needs of the current research is called secondary data. Additionally, the information is accumulated by somebody else instead of the author of the study himself. This method is also known as second-hand information. Secondary sources are utilised for the first time. Hence, it is called secondary. Valuable readings and analysis grounded on primary sources are provided by secondary sources. Secondary sources elucidate primary sources in detail and often make use of them for supporting particular research or perspective. Common kinds of secondary sources that are used by researchers in their thesis projects are as follows;
- Previous researches
- Financial sources Letters
- Diaries
- Research analysis
- Web information
- Historical data
- Encyclopaedias
- Monographs
- Journal articles
- Works of criticism and interpretation
- Biography
- Dissertations
- Official statistics
- Mass media products
- Government reports
- Google Analytics.
Pros and Cons of Secondary Data
| Pros of Secondary Data | Cons of Secondary Data |
|---|---|
|
The Data Can Be Collected by Anyone |
Out-Dated Data |
|
Low Cost or Free |
No control over the quality of data |
|
Easy to Access |
Biasness |
|
Time-saving |
Difference between Primary Data and Secondary Data
Checklist of Primary and Secondary Sources
- Secondary data should always be gathered from reliable and authentic source.
- Primary Sources require more money and time
- Consent is mandatory for participants involved in primary sources.
- Secondary Sources are quick and easy
- Ethical considerations play a vital role in both of the sources.
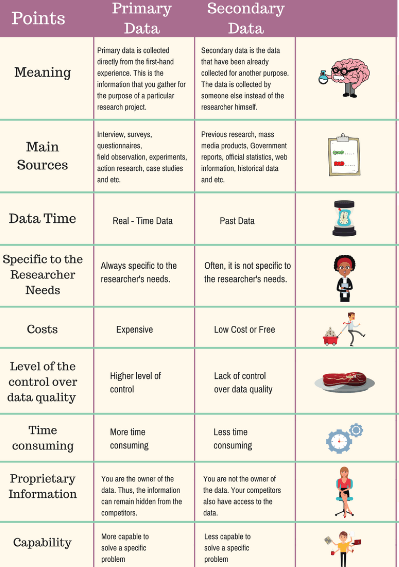
Dos and Don’ts of Primary and Secondary Sources



 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Contact
Contact Call
Call Live Chat
Live Chat